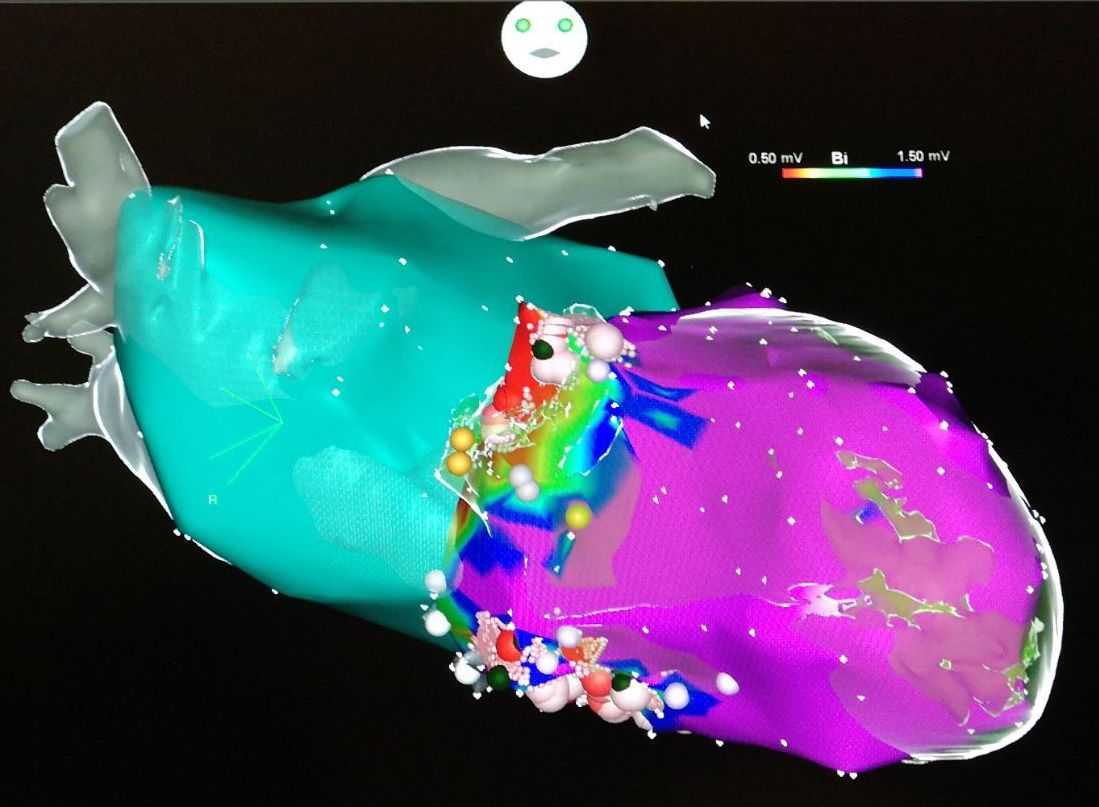
Catheter ablation is increasingly being used primarily in young patients without structural heart changes, as they do not want to take medication for the rest of their lives or because it is associated with side effects. Catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia is mainly performed endovascularly (“from the inside”), but may also be necessary epicardially. The pericardium is punctured from the outside under the sternum and the catheters are navigated in the pericardium.