In the case of advanced stage hemorrhoidal disease, a visit to the doctor’s office is always advisable. This is especially true if you discover blood in your stool. A possible contact person is your family doctor or a specialist for the rectum. Treatment depends on the extent of hemorrhoidal disease and symptoms.
Treat hemorrhoids yourself - tips
- Avoid constipation: consume enough fiber and drink plenty of fluids (1.5 to 2 liters daily). Good sources of fiber are whole grain products (rice, pasta, bread), fruit (including dried fruit), vegetables, legumes (peas, lentils, beans), seeds (linseed, psyllium) and nuts. Sufficient exercise also stimulates the bowels and counteracts constipation.
- Make sure you have healthy toilet habits: Don’t delay going to the toilet, only go when you really have to and don’t sit on the toilet for too long.
- Anal hygiene: Clean the anal region thoroughly after using the toilet. It is best to use a bidet or moisten toilet paper with water and then dry the anal area carefully. Excessive anal hygiene is counterproductive: it is better to avoid washing lotions or moist toilet paper, which often contain various irritating additives.
- Sitz baths: These are a proven household remedy for hemorrhoids. You can either use pure water for the sitz bath or add arnica, camomile, oak bark, tea tree oil or witch hazel. The substances from these plants have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Ointments: Ointments with zinc, panthenol, witch hazel or aloe vera are intended to relieve skin irritation and itching. There are also some ointments that require a prescription, for example with the active ingredient lidocaine, which has a local anesthetic effect. Ointments with cortisone are intended to slow down the inflammation. However, such ointments should only be used in the short term.
- Anal tampons and suppositories: Some active ingredients are also available in the form of suppositories or anal tampons (suppositories with gauze strips). Whether they actually help with hemorrhoids has not yet been proven.
In the case of advanced hemorrhoids and severe symptoms, self-treatment is usually no longer sufficient. Doctors have various options for improving hemorrhoidal disease. Which treatment you choose always depends on the degree of hemorrhoids.
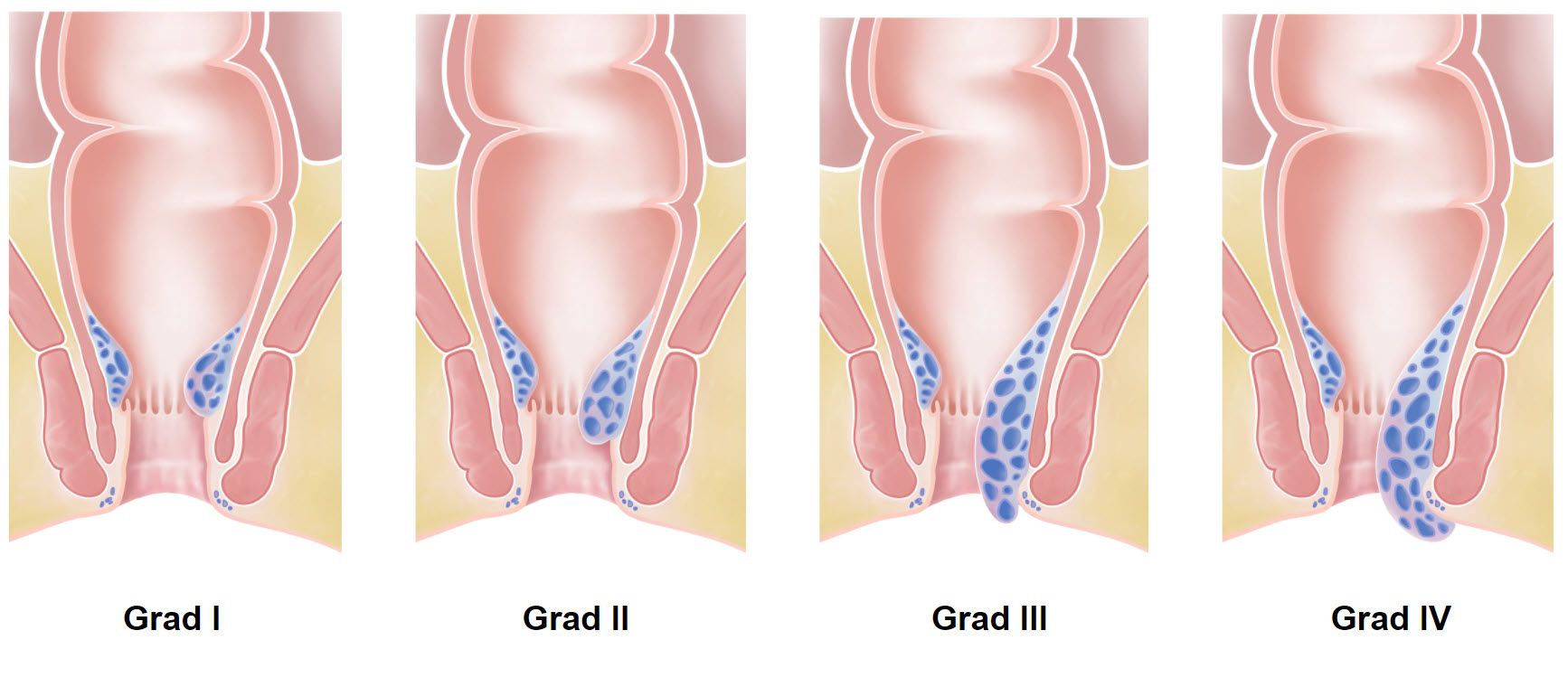
Degrees of hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are clinically classified into 4 grades.
Grade I
The hemorrhoids are located at the upper end of the anal canal and do not protrude outwards even when pressing. They can only be seen during the proctologic examination.
Grade II
The hemorrhoids protrude outwards when you push, but spontaneously retract back into the anal canal.
Grade III
The hemorrhoids protrude outwards when you push, but do not disappear spontaneously and have to be pushed back with a finger.
Grade IV
The hemorrhoids protrude outwards and can no longer be pushed back.
Hemorrhoids: Therapy
The therapy depends on the degree of hemorrhoids. In the case of 1st degree hemorrhoids, there is a chance that they will disappear after changing certain lifestyle habits. Therefore, a conservative approach with plenty of drinking, fiber and exercise is the first therapeutic approach. Psyllium seeds (e.g. Metamucil® 1-3 coffee spoons/day) and mild laxatives (Movicol® sachets 1-2/day, alternatively Transipeg® forte 1-3 sachets/day) should be used as support. Tablets (Daflon® 500mg 2x/day, alternatively Doxium® Tbl. 2x/day) or suppositories/ointments (Faktu® 3x/day) can also be helpful for bleeding. These measures also form the basis for the treatment of higher-grade hemorrhoids.
If the symptoms cannot be eliminated by these conservative measures, rubber band ligation is the method of choice for grade 2 hemorrhoids, sometimes also for grade 3. In rubber band ligation, a rubber band is applied above the hemorrhoidal cushions, thus cutting off the blood flow to the hemorrhoid. The rubber band ligation can be performed in the practice. As a rule, several ligatures are required, which are performed in several sessions. After rubber band ligation, around half of patients are free of symptoms after 10 years. In selected cases, rubber band ligation can also be used for more severe hemorrhoids.
2nd degree hemorrhoids are the main indication for so-called interventional therapies. These include infrared therapy, sclerotherapy and hemorrhoid artery ligation (HAL).
In infrared therapy and sclerotherapy, the tissue above the hemorrhoidal cushions is scarred using infrared light or certain substances (quinine-urea, phenol solution), which can lead to their shrinkage.
In hemorrhoid artery ligation (HAL), the vessels leading to the hemorrhoids are ligated with a suture. The vessels are examined with a special proctoscope. In principle, the procedure can be performed without anesthesia. Due to the length of the procedure, however, a short anesthetic is often advisable.
With 3. and 4th degree hemorrhoids surgical therapies are usually used. A basic distinction must be made here between procedures in which the hemorrhoids are completely removed and operations that do not remove the hemorrhoids.
In the classic Ferguson or Milligan-Morgan operation, the hemorrhoids are removed completely. The difference between these two operations is that the wound is closed in the Ferguson method, whereas it remains open after the Milligan-Morgan operation.
In the Longo procedure, the hemorrhoids themselves are not removed, only the mucous membrane directly above the hemorrhoids. This is done with a cutting and stapling device. By removing the mucous membrane above the hemorrhoids, the feeding vessels are severed and the mucous membrane is fixed to the intestinal wall. As a result, the hemorrhoids shrink and can no longer protrude outwards. In addition, an ‘anal lift’ is performed to a certain extent. The advantage of this method is that it is relatively painless. The patient is usually fit for work again within a week. The operation is usually performed on an outpatient basis at our clinic.
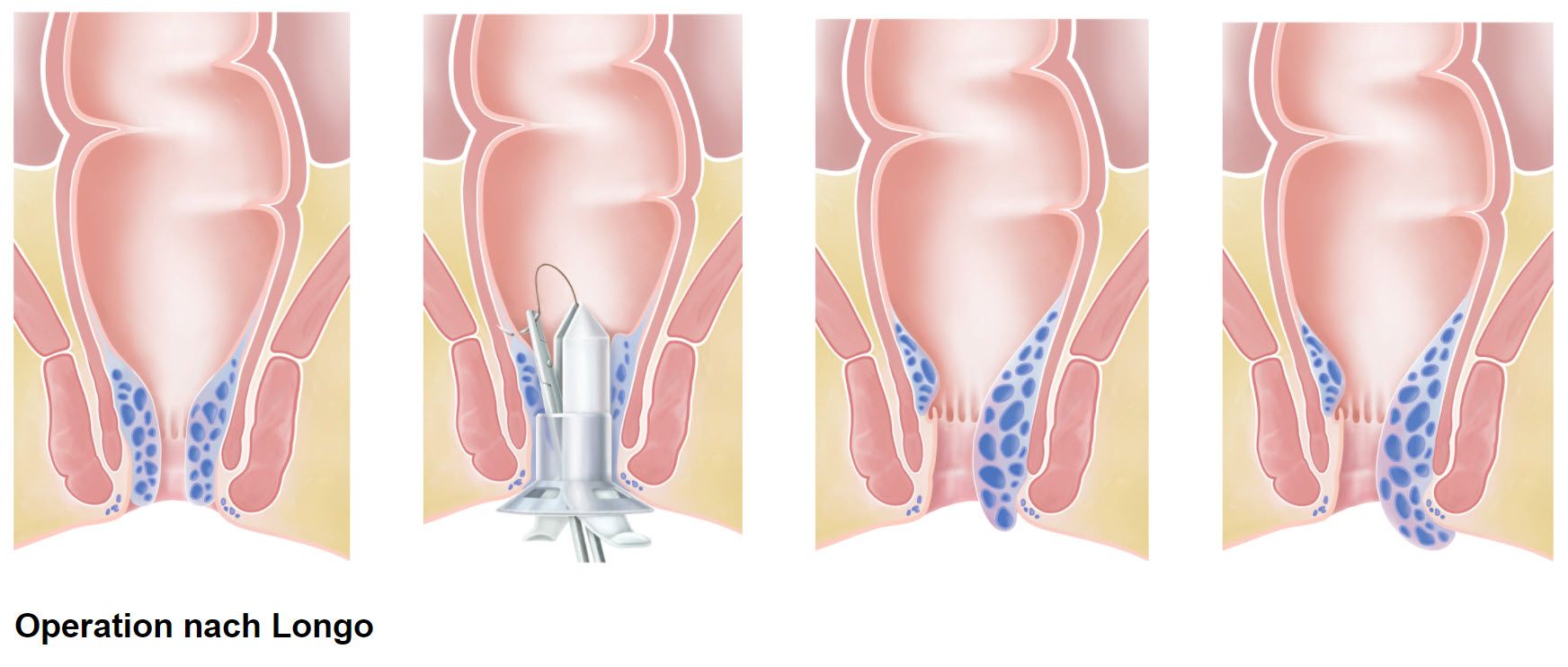
Surgical information on the Longo operation
- Preparation: small enema
- Anesthesia: general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia
- Operation duration: 30 minutes
- Hospitalization: outpatient
- Incapacity for work: 7 days
- Follow-up treatment: stool regulation



