The most frequently asked questions about fertility treatment
Many couples with an unfulfilled desire to have children have a lot of questions. We have compiled and answered the most frequently asked questions about the topic and our range of treatments for you.
Before the treatment
We recommend that you consult a fertility specialist after twelve months at the latest if you have not become pregnant. We advise couples over the age of 35 to take this step earlier.
At our university fertility center, we are able to fulfill seven out of ten couples’ wish for a baby, which is above average. However, several treatment cycles may be necessary.
However, depending on the reasons for childlessness, especially with increasing age, the chance of pregnancy may vary. In certain cases we have to advise a couple against treatment. We would be happy to inform you about your individual chances of success in an initial consultation.
There are various ways of dealing with an unfulfilled desire to have children: You can make use of our professional help. We would be happy to present the various options to you in a consultation. It is very important to us to provide you with the information you need to make the right decision for you. Of course, only you know whether and which possibilities of modern medicine you would like to use for yourself.
An egg matures in the ovary of a sexually mature woman every four weeks. This process is influenced by the female sex hormones. The egg is located in a follicle, which bursts about 14 days after the start of menstruation (ovulation) and releases the now fertilizable egg into the fallopian tube. The growing follicle produces hormones (including oestrogens, e.g. oestradiol). Thanks to these hormones, the lining of the uterus grows and the cervix opens. This makes it easier for the sperm cells (= sperm) to ascend into the uterine cavity.
After ovulation, fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube. The egg and the sperm cell, i.e. the maternal and paternal genetic material, fuse together. The cells divide, which marks the beginning of human growth. Within 4-5 days, the embryo migrates into the uterine cavity and implants in the mucous membrane. The early embryo releases signal substances (e.g. HCG) to the maternal organism. As a result, the corpus luteum formed in the ovary after ovulation is retained for 3-4 months. The hormone progesterone produced in the corpus luteum maintains the pregnancy until the child takes over all regulatory tasks itself via its placenta (= placenta).
This is the normal development of a fertilized egg in the female body:
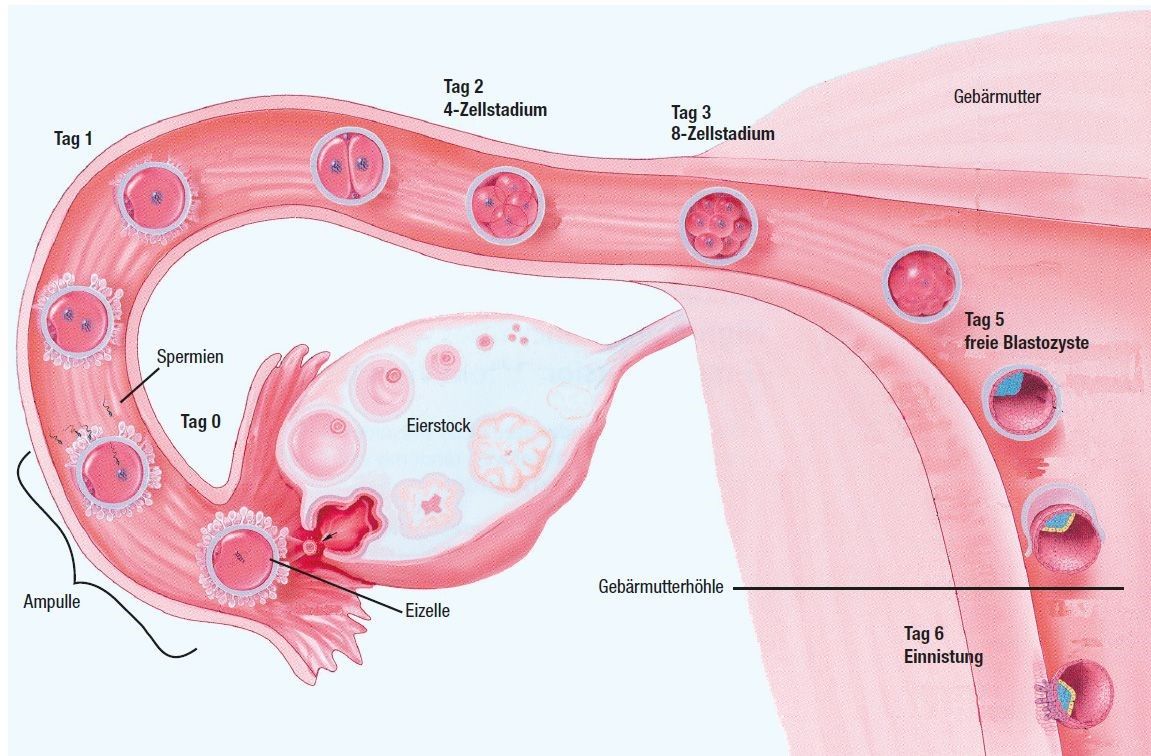
Fertilization takes place within 12 hours of ovulation in the outer end of the fallopian tube, i.e. can only occur if a sufficient number of sperm reach the egg in time.
The fertilized egg is transported through the fallopian tube into the uterus within several days. On On day 5, the embryo reaches the uterine cavity in the blastocyst stage. Implantation in the uterine lining takes place on 6th day after fertilization.
Implantation
Both when the egg is fertilized in the fallopian tube and when embryos are transferred to the uterus through the cervix after IVF or ICSI treatment, the embryo first rolls over the uterine lining. Both the embryo and the uterine lining release substances that ultimately determine the ideal implantation site. As soon as the embryo has made contact there, it is increasingly surrounded by mucosal tissue to ensure perfect nourishment. Today it is assumed that successful implantation is influenced more by the embryo than by the mucous membrane.
During the treatment
If our examinations show that there was no normal egg maturation in the cycle in question, we do not perform a follicular puncture due to the low chances of success.
Overstimulation is the displacement of tissue water and blood salts into body cavities. It mainly occurs in women with a large number of follicles after stimulation treatment. The hyperstimulation syndrome only occurs after egg retrieval, is usually most pronounced about a week after egg retrieval and disappears with the bleeding about 14 days after egg retrieval. Today, however, we have treatment protocols that reduce the risk of hyperstimulation syndrome to almost zero. As pregnancy perpetuates hyperstimulation syndrome, it may be advisable to use a special treatment if the risk is particularly high. it makes sense to refrain from embryo transfer directly after stimulation treatment. In most cases, hyperstimulation syndrome is rather mild and can be easily checked on an outpatient basis using blood tests and ultrasound measurements. In a few cases (< 1:100) the course is more severe and abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting occur. Occasionally a stay in hospital is then necessary.
A follicular puncture is a surgical procedure. In rare cases, abdominal organs or blood vessels may be injured. The doctor then has to open the abdominal cavity and surgically treat the injury. Such a complication occurs in far less than 1 in 1000 punctures. To ensure that we are prepared for this emergency, we prepare all patients for anesthesia at our fertility center.
Despite the very good chances of success at our university fertility center, we unfortunately do not achieve a pregnancy in every treatment cycle. It is possible, for example, that the egg does not fertilize or does not develop after fertilization. However, these difficulties are not caused by the treatment, but primarily by the generally low fertility of humans.
The transfer of two embryos increases the chance of pregnancy compared to the transfer of only one embryo. However, this can lead to twins and consequently more premature births. This fact must be taken into account when deciding on the number of embryos to be transferred.
The risk of miscarriage is not increased when maternal age is taken into account. There is an ectopic pregnancy risk of around 5 percent if the fallopian tubes are altered.
The birth weight of children after IVF or ICSI is slightly lower than usual. It is possible that the risk of malformation is slightly increased. Recent studies indicate that children from the early years of IVF may be more prone to higher weight and blood pressure in later life. Pregnancy complications – such as placenta praevia – are also somewhat more common. However, it is known that many of these problems are related to involuntary childlessness itself and not to the treatment methods IVF or ICSI.
After ICSI, special changes in the genetic material (chromosomal aberrations) can occur if the sperm quality is severely impaired.
occur somewhat more frequently. At the couple’s request, prenatal diagnostics can provide clarity from the 11th week of pregnancy. Furthermore, after ICSI, a male offspring can have the same fertility problems as his father.
An IVF or ICSI treatment cycle takes 2-3 weeks. In addition, depending on the protocol, a pre-treatment of 2-4 weeks is added. With
no visit to the doctor is necessary for pre-treatment. During hormonal stimulation, 2-3 controls are usual. We can determine the exact dates together with you when you register for the start of IVF/ICSI at the beginning of your period.
As a rule, the preliminary clarifications for fertility treatment are completed within 1-2 cycles.
Most women tolerate IVF/ICSI treatment better than expected. Irritability may occur during the preparation phase – however, most women do not notice any changes. The actual stimulation phase is very well tolerated by the vast majority of women – although the injection is of course unpleasant. Further details can be found in the questions above. We are also happy to advise you on special concerns.
Questions and answers on stimulation
For you: Please continue to take thyroid medication, e.g. Euthyrox tablets and folic acid or a multivitamin preparation for pregnancy.
Dafalgan or paracetamol can be used as painkillers during stimulation. Please discuss all other medications directly with your doctor.
For him: Please do not take any antibiotics or ibuprofen in the three months prior to fertility treatment.
You may have unprotected sexual intercourse until the 6th day of the stimulation phase. 2-3 days later you come for an ultrasound appointment. Please discuss the further procedure with the doctor there
We recommend a healthy, balanced diet. You do not need to abstain from raw meat or raw milk cheese during stimulation, as you are not yet pregnant. However, we already advise against drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes.
Yes, you are also welcome to be active during the stimulation phase. However, from the 6th day of stimulation, when the ovaries become larger, you should avoid sudden movements (tennis, jogging, etc.). Please always protect your abdomen/abdominal area.
The information sheet “Most important information on the stimulation procedure”, which you received in the white folder when planning your treatment, contains the start and end dates of the intake/application that have been personally determined for you.
Yes, during this time, bleeding is more frequent and can be as heavy as menstrual bleeding. This is normal and no cause for concern.
The medication must be injected for at least 9 days. During the ultrasound examination, the doctor will discuss with you whether and for how long the injections should be continued.
Injecting into the thigh is much more comfortable than injecting into the abdomen. The absorption and effect of the medication is very reliable.
Costs and organizational matters
The costs of the assessment are covered by the health insurance companies. Hormone treatments to support egg maturation with timed intercourse or intrauterine inseminations (IUIs) are covered by your health insurance for up to a maximum of one year and three inseminations before the woman’s 40th birthday, depending on the product chosen.
In the case of in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), you are responsible for the treatment costs from the start of hormone treatment. You can expect to pay between CHF 5,000 and CHF 8,000 per treatment cycle at our university fertility center, depending on the cost. A treatment cycle includes the implementation and monitoring of hormone therapy (stimulation), egg retrieval (puncture), cultivation of eggs and embryos (laboratory) and transfer of the embryos into the uterus (transfer). In addition, there are any costs for freezing (cryopreservation) and storing surplus fertilized eggs/embryos of CHF 700 and the annual storage fee of CHF 400. We need hormones to mature the egg cells (stimulation). The additional costs for this amount to CHF 1,000 to 2,000, depending on the product and the quantity of hormone required.
At the start of treatment, we will arrange the appointments with you. You know several weeks in advance exactly when you need to come for a check-up and how much time it will take. This approach allows you to plan in good time, which is also important for your professional life.
We attach great importance to constant medical care. The senior physician in charge of your case will introduce herself to you at the initial consultation. She is responsible for your treatment, but also for your concerns and answering your questions. She is supported by an experienced assistant doctor and a competent and empathetic nursing team.
At the University Hospital Zurich, we naturally adhere strictly to the requirements of the Swiss Reproductive Medicine Act (FMedG). This is confirmed by the regular cantonal medical inspections.
We are constantly improving the quality of our treatment processes. As an expression of our success, our fertility center is certified according to the ISO 9001:2015 quality management system and our laboratories are accredited according to ISO/IEC 17025.
Our fertility center is a founding member of FIVNAT-CH, Switzerland’s national IVF data register, which has been in existence since 1993. On behalf of the Federal Statistical Office, FIVNAT-CH collects and checks various anonymized key figures for each cycle performed at all Swiss fertility centers. We are regularly among the centers with the very best pregnancy rates in Switzerland. Independent international experts periodically check the accuracy of the data we report (external audits).
You can find all our current certificates on the Reproductive Endocrinology Clinic page.
Requirements for fertility treatment in Switzerland
The Swiss Reproductive Medicine Act requires you to be in a stable relationship in order to undergo fertility treatment. However, you do not have to be married.
Ideally, both partners should be able to accompany the future child until the age of 18. In the event of any illnesses that could prevent this situation, we carefully check with the specialist colleagues treating you whether and how we can improve the conditions for parenthood.
While there are no legal restrictions on the age of treatment, nature sets limits to the chances of success of fertility treatment. We therefore generally offer in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injections (ICSI) up to the woman’s 43rd birthday. Only in a few exceptional cases with above-average prerequisites does it make sense to exceed this limit by a maximum of 1-2 years – we would be happy to look at this together with you.
To prevent such a situation, social freezing is a valuable option today.
If you have not frozen your own eggs, egg donation abroad may be an alternative, as Swiss legislation does not currently permit egg donation in Switzerland.
As obesity is associated with both reduced chances of pregnancy and increased pregnancy risks for mother and child, a normal weight is recommended at the start of fertility treatment. As being significantly overweight can also make egg retrieval difficult or impossible, we recommend that you lose weight sensibly at an early stage. The focus here is on the state of health and not the absolute weight.
